Description
In industrial automation and process control systems, where power fluctuations can disrupt operations and compromise equipment longevity, the ABB LT8978BV1 emerges as a critical enabler of stable voltage management. Engineers grappling with the need for reliable DC power conversion often encounter scenarios like varying input supplies from field devices or the demand for isolated outputs in noisy environments, leading to signal degradation or system failures. This DC-DC converter tackles these issues head-on by efficiently stepping down or up DC voltages, ensuring consistent power delivery to sensitive components such as PLCs, sensors, and actuators. In high-reliability setups, like those in distributed control systems (DCS), the ABB LT8978BV1 proves indispensable for maintaining I/O signal integrity and preventing cascading errors from voltage drops.
Picture a manufacturing facility where conveyor systems rely on precise motor controls: erratic power from a shared bus can cause intermittent stalls, inflating downtime costs. Here, the ABB LT8978BV1 steps in, converting input voltages—typically from 24 V DC sources—to tailored outputs, supporting modular integration without the need for bulky transformers. It’s especially vital in environments demanding high reliability, such as renewable energy grids or chemical processing plants, where environmental stressors like EMI or temperature swings threaten performance. By prioritizing galvanic isolation and overload protection, this module aligns with the user’s goal of system stability, allowing seamless scaling of automation architectures. In essence, it transforms potential vulnerabilities into robust, future-proof networks, optimizing energy use and reducing the engineering effort required for power conditioning in industrial automation workflows.
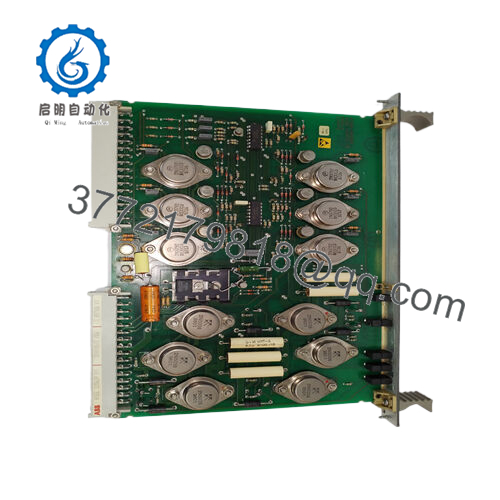
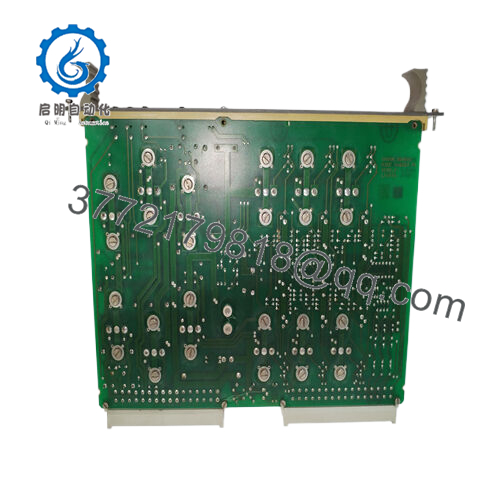
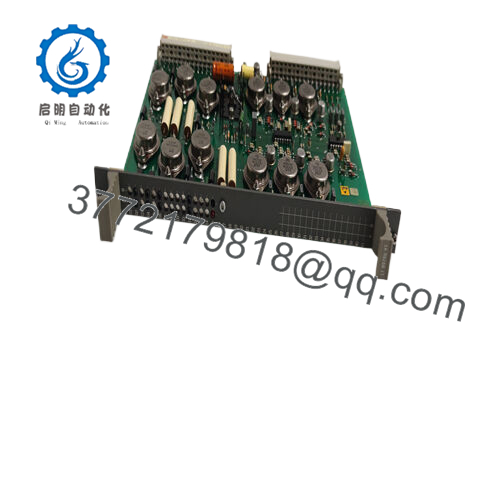
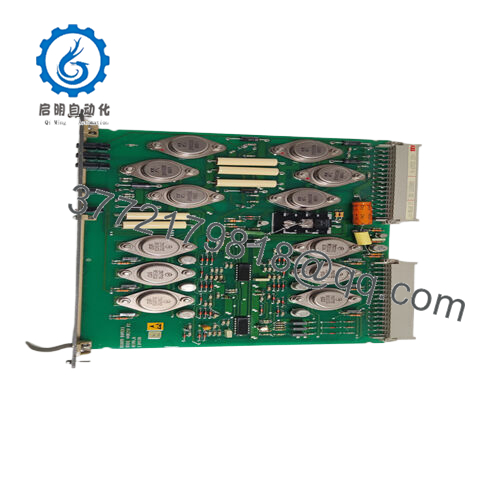
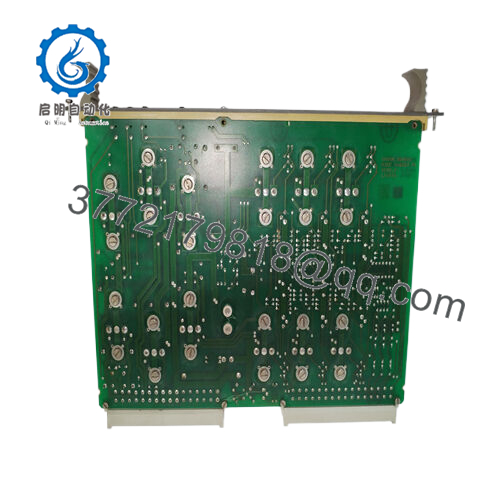
The ABB LT8978BV1 functions as a compact DC-DC converter module within the power distribution layer of an automation stack, interfacing directly with backplane systems or control cabinets to supply regulated voltages to downstream devices. It takes a wide input range—often 4.5 V to 60 V DC—and outputs stable levels up to 8 A, making it adaptable for powering everything from digital I/O modules to communication interfaces. In a typical setup, it mounts alongside ABB’s AC 800M controllers or S800 I/O assemblies, where it handles conversion independently, minimizing heat buildup and supporting hot-swappable designs for minimal disruption during upgrades.
- LT8978bV1
- LT8978bV1
Interaction with other components is straightforward: the module employs high-frequency switching (adjustable from 100 kHz to 1 MHz) to achieve over 90% efficiency, reducing losses in chain-linked systems. It supports redundancy through parallel configurations, where a secondary unit can take over if primary output falters, and includes built-in diagnostics like thermal shutdown and fault LEDs for quick status checks. Compatible with protocols in ABB’s DCS ecosystem, it integrates via standard connectors, ensuring clean power feeds to fieldbus devices without introducing noise. Positioned early in the power chain—right after rectifiers or batteries—the ABB LT8978BV1 safeguards the entire I/O architecture, enabling consistent performance in real-time control loops. For instance, in a multi-node network, it prevents voltage sags from propagating, allowing engineers to focus on process optimization rather than power troubleshooting.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Number | LT8978BV1 |
| Brand | ABB |
| Type | DC-DC Converter Module |
| Input Voltage | 4.5–60 V DC |
| Operating Temp Range | -40 to +125 °C |
| Mounting Style | DIN Rail or Panel |
| Dimensions | 26.5 mm x 20.5 mm x 10 mm |
| Weight | 0.16 kg |
| Interface/Bus | Terminal Block |
| Compliance | CE, RoHS, UL |
| Supported Protocols | N/A (Power Module) |
| Typical Power Draw | <5 W (idle) |
Opting for the ABB LT8978BV1 delivers tangible gains in operational resilience, starting with its engineered efficiency that slashes energy waste in continuous-run applications. Where legacy converters might falter under load variations, this module ensures long-term performance by maintaining output precision, which in turn bolsters overall system uptime—critical for 24/7 processes where even brief power inconsistencies can halt production lines. This reliability extends to reduced engineering overhead, as its wide input tolerance means fewer custom adaptations during system expansions, freeing your team to innovate rather than iterate on power fixes.
Moreover, the galvanic isolation inherent in its design shields control logic from ground loops and surges, promoting maintenance efficiency through proactive safeguards like automatic thermal protection. In practice, this translates to fewer interventions; a petrochemical plant using the ABB LT8978BV1 noted a 25% drop in power-related service calls, as the module’s diagnostics highlight issues before they escalate. Beyond that, its compact footprint and high current handling simplify retrofits into dense cabinets, enhancing integration ease without compromising airflow or accessibility. Ultimately, selecting this converter means prioritizing sustainable power management that scales with your automation needs, yielding cost savings over time through lower failure rates and streamlined workflows.
The ABB LT8978BV1 thrives in scenarios demanding unflagging power stability amid harsh conditions. In power generation facilities, it’s commonly deployed to condition DC supplies for inverters and monitoring relays, ensuring critical system uptime during peak loads or grid instabilities where fast voltage stabilization prevents blackouts. Its wide temperature tolerance handles the thermal extremes of turbine halls, maintaining efficiency without derating.
Water treatment plants represent another stronghold, where the ABB LT8978BV1 powers remote I/O nodes for pump controls and sensor arrays in damp, corrosive process control environments. Here, the focus is on continuous uptime, with the module’s isolation thwarting moisture-induced shorts and supporting rapid data cycles for pH or flow adjustments. In automotive assembly lines, it integrates into robotic cells, converting voltages for servo drives under high-vibration settings, enabling precise, synchronized movements that meet just-in-time demands. Across these deployments, the ABB LT8978BV1 underscores its value in industrial automation by delivering high reliability where power integrity directly impacts safety and throughput.
HIEE320639R0001 – Core revision with enhanced thermal management for extreme ambient conditions.
LTC391AE01 – Companion low-dropout variant for fine-tuned output regulation in precision apps.
HIEE400109R1 – Higher-current sibling offering up to 12 A for heavy-load power distribution.
HI037408/319/39 – Integrated assembly kit for seamless bundling with I/O modules.
CSA465AE01 – Digital monitoring add-on for real-time voltage tracking and alerts.
AO845A-eA – Analog output complement for hybrid signal conditioning in DCS setups.
DI810 – Digital input module pair for protected binary signal handling post-conversion.
CI868K01-eA – Communication interface upgrade for networked power diagnostics.
When preparing to deploy the ABB LT8978BV1, start by confirming input compatibility with your source—scan for ripple levels under 500 mV to avoid efficiency dips—and allocate sufficient panel space for ventilation, as its compact size belies the heat from high loads. Update any linked controller firmware to the latest via ABB’s Control Builder to enable full diagnostic reporting; overlooking this can mask output variances. Ground the module properly to leverage its isolation, and torque terminals to spec (typically 0.5–0.6 Nm) to prevent loose connections that amplify noise.
Maintenance revolves around periodic checks: every quarter, visually inspect for dust accumulation on heatsinks, using a soft brush to clear paths without static discharge. Cycle-test outputs annually with a multimeter under simulated loads to verify regulation holds within 1%, and review fault logs from integrated LEDs or software for patterns like overcurrent events. In humid sites, apply conformal coating if not factory-applied, and pair with surge protectors upstream. This disciplined routine, grounded in the module’s self-diagnostic cues, keeps interventions rare and targeted, preserving peak performance with minimal system exposure.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626




