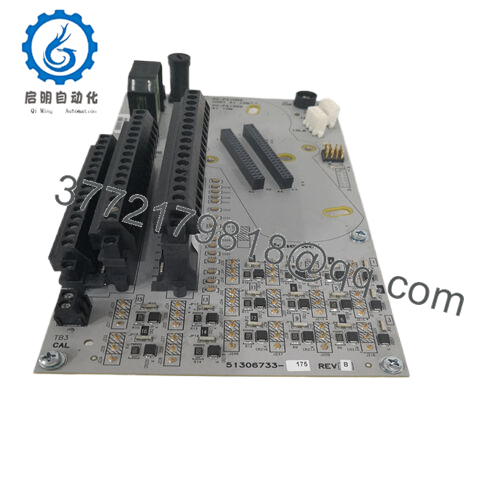
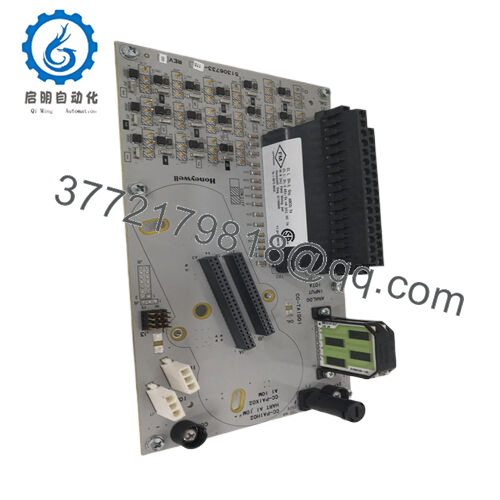
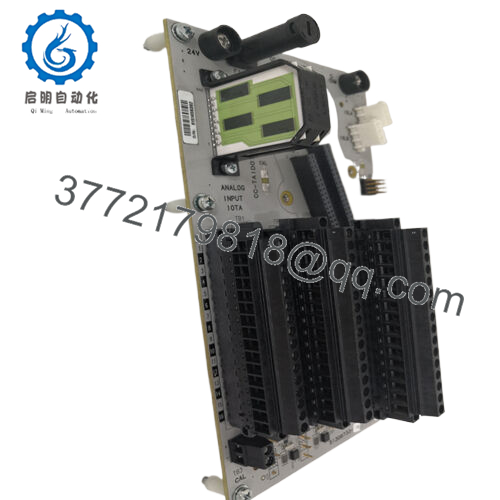
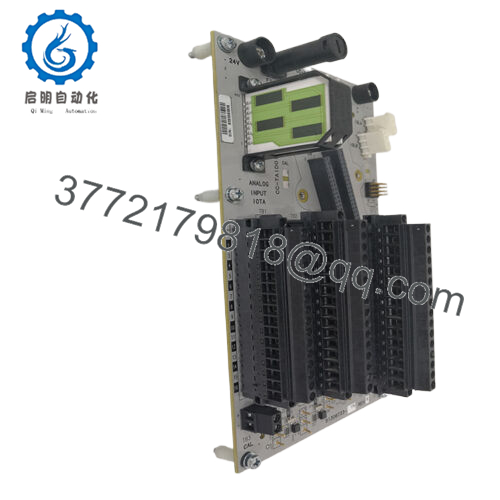
Description
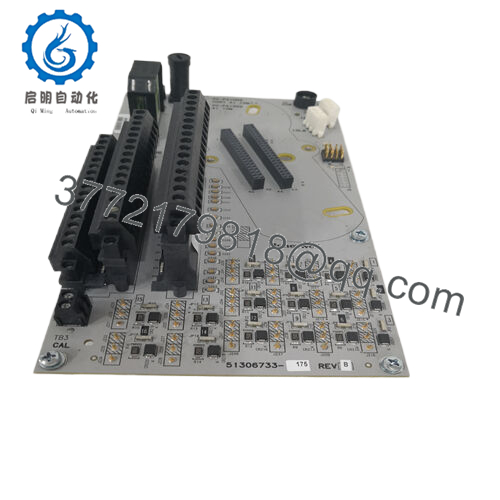
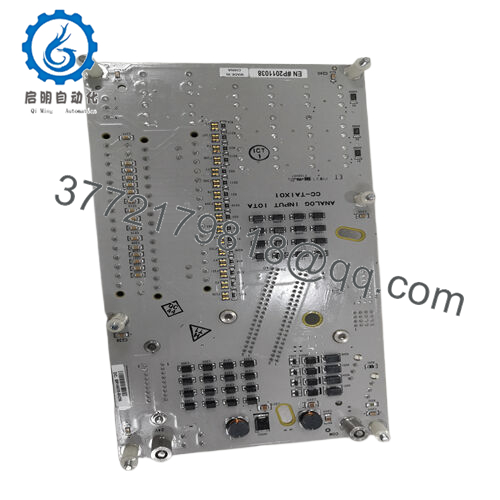
Product Model: CC-TAID01
Product Brand: Honeywell
Product Series: Series-C / IOTA Analog Input Modules
Key Features (inferred):
- Differential analog input capability (measures signal difference between two wires)
- Likely supports 4–20 mA inputs in differential mode, with built-in isolation
- Fits into Honeywell’s Experion / Series-C I/O architecture (IOTA type modules)
- Complements other IOTA modules such as CC-TAIX01 (standard analog input) and CC-TAID11 (redundant/differential variant)
- CC-TAID01
Role & System Fit
Within Honeywell’s Experion / Series-C I/O framework, “IOTA” modules serve specialized measurement or interface roles—analog input, analog output, digital I/O, etc. The designation CC-TAID01 strongly suggests it is an Analog Input (AI) IOTA module with Differential (ID) functionality. In effect, it is a module intended to measure differences between two input signals, rather than measuring each signal relative to a common return.
Differential input modules are especially useful where ground loops, common-mode noise, or long cable runs could degrade measurement quality. By measuring the difference between two lines, the module inherently rejects common-mode interference.
Because Honeywell also lists CC-TAIX01 as a standard analog input (single-ended) IOTA module in their parts catalogs and in the Series-C I/O specification documentation (EP03-490-520) the CC-TAID01 is likely its differential counterpart in the same product line (IOTA analog input modules). In some vendor listings, modules labeled “CC-TAID11” are differential analog input IOTAs (redundant version)
Thus CC-TAID01 may be the non-redundant, differential version.
In your control rack or I/O bay, the CC-TAID01 module would be inserted into a slot adjacent to analog channels and connected to field wiring via the I/O termination assembly. It then delivers clean differential analog readings to the DCS or control logic, managing noise rejection and signal integrity.
Technical Features & Benefits
Below is a plausible outline of features and benefits for CC-TAID01, based on analogous modules in the same family:
Differential Input Mode & Noise Rejection
- The key distinction is differential input—the module reads the voltage or current difference between two leads (A–B) rather than referencing a common return.
- That configuration boosts immunity to ground offsets and common-mode disturbances, especially over long wiring or in electrically noisy environments.
- Channels wired as differential pairs can reject interference equally present on both lines, improving signal fidelity.
Input Type & Ranges
- As an analog input IOTA, CC-TAID01 likely supports standard industrial ranges, e.g. 4–20 mA, 0–5 V, 1–5 V, or other voltage ranges, but configured in differential mode.
- It may have internal resistors or load elements to accommodate current loops.
- Input impedance in differential mode is usually high, to avoid loading the transmitters.
Isolation & Safety
- To maintain safe separation, the module probably provides galvanic isolation between field inputs and internal backplane or logic circuits.
- It may support a certain isolation voltage (e.g. 1,500 VAC or more) to protect from surges or ground faults.
- The design may include diagnostics for wire faults (open-wire, short-wire) and status indication per channel.
Integration and Compatibility
- It fits into the IOTA / Series-C analog I/O stack governed by the Experion / C300 rack architecture.
- It likely conforms to the I/O specification families described in Honeywell’s EP03-490-520 (Series-C I/O spec)
- Configuration, scaling, and fault handling integrate into the DCS’s HMI / control logic environment.
Performance & Accuracy (Estimated)
Based on similar modules in the same family (e.g. CC-TAID11), performance might include:
- 16-bit resolution or similar high granularity
- Accuracy on the order of ±0.05 % to ±0.1 % of full scale
- Signal filtering or averaging to stabilize reading over noise
- Channel update or scan times compatible with control system expectations
The differential mode tends to degrade noise performance less than single-ended modes, so the module might offer better effective accuracy when properly wired.
Technical Specifications Table (Estimated)
Here’s a suggested spec table — treat these values as placeholders until confirmed from your unit:
| Specification | Estimated Value / Range | Comment / Assumption |
|---|---|---|
| Model | CC-TAID01 | — |
| Function | Differential Analog Input IOTA Module | Differential (ID) variant of IOTA analog input |
| Number of Channels | ~16 channels (or same as other analog IOTAs) | Many IOTA AI modules are 16-channel variants |
| Input Types | Differential 4–20 mA, ± voltage ranges | Supports differential measurement |
| Common-Mode Range | ±10 V to ±15 V or more | So module can tolerate ground offsets |
| Input Impedance | High (≥ 50 kΩ or more) | Minimal load on transmitter |
| Resolution | 16 bits (or equivalent) | High precision analog conversion |
| Accuracy | ~ ±0.05 % to ±0.1 % FS | Comparable to sibling modules |
| Isolation | ≥ 1,500 VAC field to internal | Ensures safety between field and logic |
| Scan / Update Time | ~50 ms (or similar AI module speed) | Typical for many analog I/O modules |
| Power Consumption | Modest (few watts) | Similar to other IOTAs |
| Interface | Backplane IOTA interface, configuration via DCS | Integrated into rack |
| Environmental | Standard industrial (-20 to +60 °C, etc.) | Under I/O spec standards |
Again, these are inferred. When you get your module, check its label for revision, input ranges, and wiring instructions.
Installation & Maintenance Insights
Here are field tips if you work with the CC-TAID01 module:
Wiring Configuration & Setup
- Ensure proper pairing of differential lines (i.e. signal + and signal –). Mis-wiring will distort readings.
- Use twisted shielded pairs and avoid routing near high-voltage or noisy cables.
- Verify that your upstream configuration (DCS or I/O setup) is set to differential mode for the channel(s). If you accidentally leave a channel in single-ended mode, readings will be incorrect.
- Watch for ground offsets: differential mode tolerates some offset, but large mismatches might exceed common-mode rejection limits.
Commissioning & Calibration
- After powering up, verify channel readings using a precision source (e.g. apply 4 mA, 12 mA, 20 mA across differential wires) and confirm linearity.
- Use diagnostics in the control system to check for open-wire, short-wire, stuck channels, or channel faults.
- Monitor common-mode voltages occasionally; limit drift to within module tolerance.
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
- If a channel gives erratic behavior, check for asymmetry or interference on one side of the pair.
- For channels that appear “dead,” measure across both lines to see if there’s a wiring fault.
- When replacing the module, ensure configuration, scaling, and fault logic are fully migrated.
- Keep the module and connector pins clean; dust or corrosion can degrade differential performance.
Spare & Redundancy Strategy
- Keep at least one spare CC-TAID01 (or matching revision) in stock — differential modules are more specialized and replacement can be time-sensitive.
- Label channels and wiring strongly so when swapped, no wires are misconnected.
- Test spares offline (simulate differential inputs) before deploying in process.
Related Modules / Family
Here are some sibling IOTA modules you might encounter:
- CC-TAIX01 — the standard analog input (single-ended) IOTA module, widely documented and used
- CC-TAID11 — the redundant or higher-spec differential analog input IOTA (used in high-availability setups)
- Analog Output IOTAs (e.g. CC-TAOX01, CC-TAON01) for analog output rather than input
In many implementations, differential and single-ended analog inputs co-exist, so your control configuration must support both types properly.






 WhatsApp: +86 16626708626
WhatsApp: +86 16626708626 Email:
Email:  Phone: +86 16626708626
Phone: +86 16626708626



